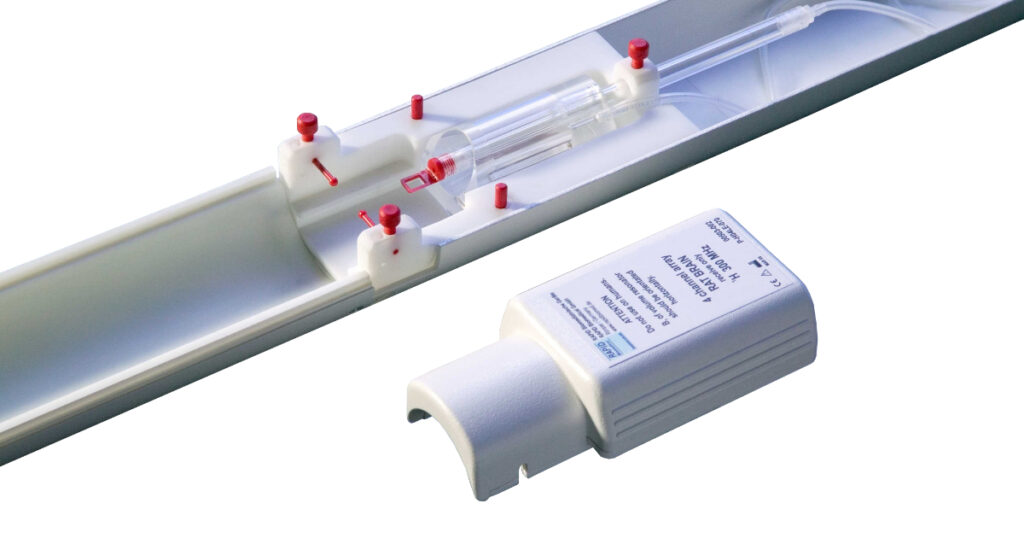
Rat Head Phased Arrays
Description
- surface coil array for 1H imaging of small animals
- 2-channel and 4-channel* version available
- anatomical shape for optimized receive homogeneity and SNR
- supporting parallel imaging experiments
- mechanically adapted to RAPID rat holder LHRXGS-00563
- compatible with both dedicated animal or whole body scanners to allow pharmacological studies on contrast agents at a field strength of clinical relevance
- available for non-proton studies upon request
- measurements: down to 50 mm x 16 mm
- pre-requisites:
– 2- resp. 4-channel receiver system
– pin diode driver (if applicable)
– actively decoupled volume transmit coil
Individually adaptable to the established systems like Bruker, Agilent, Varian and clinical scanners at any field strength.
Please contact us for availability on your NMR system.
Publications
P. Wespi, J. Steinhauser, G. Kwiatkowski, and S. Kozerke: High‐resolution hyperpolarized metabolic imaging of the rat heart using k–t PCA and k–t SPARSE.
NMR in Biomedicine, 31:e3876, doi: 10.1002/nbm.3876 (2018)
with RAPID Biomedical dual tuned 13C transmit coil V-XLS-HL-094-00937 and 2-channel 13C rat head receive array # P-X02LE-094-00938
J. Steinhauser, P. Wespi, G. Kwiatkowski, and S. Kozerke: Assessing the influence of isoflurane anesthesia on cardiac metabolism using hyperpolarized [1‐13C]pyruvate.
NMR in Biomedicine, e3856. doi: 10.1002/nbm.3856 (2017)
with RAPID Biomedical dual tuned 13C transmit coil V-XLS-HL-094-00937 and 2-channel 13C rat head receive array # P-X02LE-094-00938
P. Wespi, J. Steinhauser, G. Kwiatkowski, and S. Kozerke: Overestimation of cardiac lactate production caused by liver metabolism of hyperpolarized [1-13C]pyruvate.
Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, doi: 10.1002/mrm.27197 (2018)
with RAPID Biomedical dual tuned 13C transmit coil V-XLS-HL-094-00937 and 2-channel 13C rat head receive array # P-X02LE-094-00938
J.-F. Thibodeau et.al.: Vascular Smooth Muscle-Specific EP4 Receptor Deletion
in Mice Exacerbates Angiotensin II-Induced Renal Injury.
ANTIOXIDANTS & REDOX SIGNALING, Volume 25 / Number 12, doi: 10.1089/ars.2015.6592, 642-657 (2016)
with RAPID Biomedical 4-channel rat head array # P-H04LE-070-01193
G.O. Cron et.al.: Patients with High Blood Pressure Should Avoid Aspirin: Reduced Renal Perfusion in Hypertensive EP4 Knockout Mice.
Proc. Intl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Med., 23, 1575 (2015)
with RAPID Biomedical 4-channel rat head array # P-H04LE-070-01193
J. Ramu et.al.: Longitudinal diffusion tensor imaging of the rat brain after hexachlorophene exposure.
Elsevier NeuroToxicology,56, 225–232 (2016)
with RAPID Biomedical 4-channel rat head array # P-H04LE-070-01276
J. Bolcaen et.al.: 18F-fluormethylcholine (FCho), 18F-fluorethyltyrosine (FET), and 18F-fluordeoxyglucose (FDG) for the discrimination between high-grade glioma and radiation necroses in rats: A PET study.
Nuclear Medicine and Biology, doi.org/10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2014.07.006 (2014)
with RAPID Biomedical proton transmit volume coil # V-HLS-070-01405 and proton 2-channel rat head coil # P-H02LE-070-00879
J. Bolcaen et.al.: MRI-guided 3D conformal arc micro-irradiation of a F98 glioblastoma rat model using the Smal Animal Radiation Research Platform (SARRP).
J Neurooncol, 120:257–266, DOI 10.1007/s11060-014-1552-9 (2014)
both with RAPID Biomedical volume transmit coil # V-HLS-070-01405 V01 and 2-channel rat head array # P-H02LE-070-00879